Nation-state cyberattacks are a growing threat in the 21st century, impacting businesses, critical infrastructure, and even democratic processes. Understanding the evolving threat landscape and taking proactive steps to strengthen cybersecurity defenses is crucial for mitigating these geopolitical risks.
-
Nikita Alexander
- February 21, 2025
- 6 minutes

The digital realm has become a new battleground. No longer are geopolitical tensions confined to traditional warfare; they now spill over into cyberspace with increasing frequency and ferocity. Nation-state cyber threats, once a shadowy concern, have emerged as a significant and persistent risk, impacting businesses, critical infrastructure, and even democratic processes across the globe, particularly within the US, UK, and EU. This evolving landscape demands a heightened awareness and a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
- Increased interconnectedness: Our reliance on digital technologies has created a vast attack surface. From critical infrastructure like power grids and hospitals to financial systems and government networks, everything is potentially vulnerable. This interconnectedness means that an attack in one sector can have cascading effects across multiple sectors, amplifying the impact.
- Lower barrier to entry: While sophisticated attacks require significant resources, the barrier to entry for less complex attacks has lowered. Nation-states can leverage readily available tools and even outsource some operations to hacktivist groups or criminal organizations, making attribution more difficult and adding a layer of deniability.
- Geopolitical tensions: Rising geopolitical tensions, whether between established powers or regional rivals, often manifest in cyberspace. Cyberattacks offer a way to inflict damage without crossing the threshold of conventional warfare, making them an attractive tool for state actors.
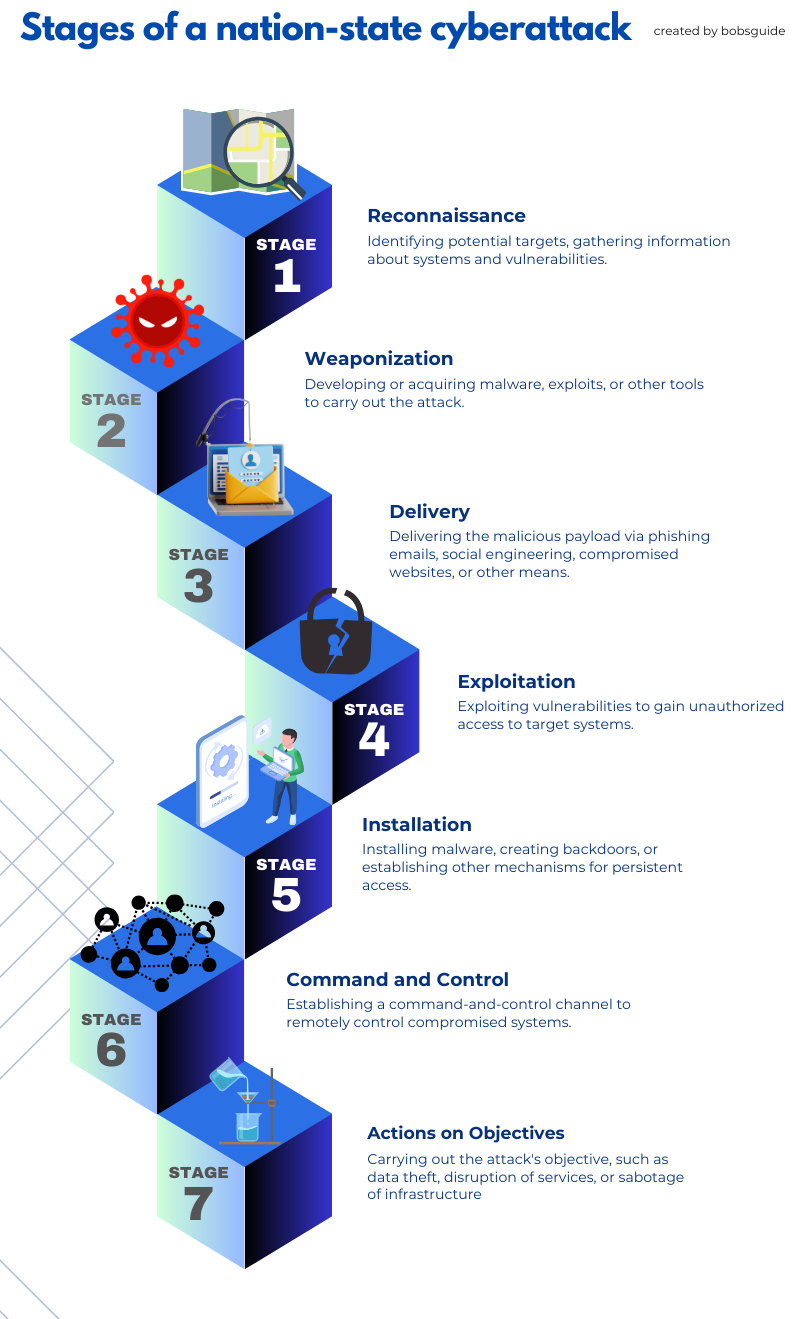
The threat landscape:
The threat landscape is complex and constantly evolving. Several nation-states are actively engaged in cyber operations, each with their own motives and targets. While attribution can be challenging, cybersecurity experts and intelligence agencies have identified several key players:
- Often associated with sophisticated and aggressive cyber operations, Russia has been linked to attacks on critical infrastructure, disinformation campaigns, and election interference. The 2017 NotPetya ransomware attack, which affected businesses worldwide, is widely attributed to Russia, although the Kremlin denies involvement. This attack, while ostensibly targeted at Ukraine, demonstrated the global reach and indiscriminate nature of some nation-state cyber operations.
- China’s cyber activities are often focused on economic espionage and intellectual property theft. Chinese state-sponsored hackers have been accused of targeting industries ranging from aerospace and defense to technology and pharmaceuticals. The theft of sensitive data from the US Office of Personnel Management in 2015, which compromised the personal information of millions of government employees, is a prime example of China’s cyber capabilities.
- Iran has also increased its cyber activities in recent years, often targeting its regional rivals and countries perceived as adversaries. Iranian hackers have been linked to attacks on critical infrastructure, including oil and gas companies, and have also engaged in disruptive attacks such as website defacement and denial-of-service attacks.
- North Korea’s cyber program, while less sophisticated than some other nation-states, has proven to be highly effective. The country has used cyberattacks to generate revenue, disrupt financial systems, and target its geopolitical foes. The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, which affected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide, is believed to have originated from North Korea.
Impact on businesses, beyond data breaches
The impact of nation-state cyber threats on businesses goes beyond traditional data breaches. Companies now face a range of risks, including:
- Disruption of operations: Cyberattacks can cripple critical systems, halting production, disrupting supply chains, and impacting customer service. A ransomware attack, for example, can encrypt critical data, rendering it inaccessible and bringing business operations to a standstill.
- Financial losses: The costs associated with recovering from a cyberattack can be substantial, including the cost of incident response, data recovery, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Furthermore, businesses may suffer reputational damage, leading to lost revenue and market share.
- Intellectual property theft: Nation-state-sponsored hackers often target businesses to steal valuable intellectual property, giving their own companies a competitive advantage. This can stifle innovation and undermine a company’s long-term prospects.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities: Cyberattacks can target a company’s suppliers, creating a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. A successful attack on a key supplier can disrupt production and delivery, impacting multiple businesses downstream.
Protecting against nation-state cyber threats:
Combating nation-state cyber threats requires a multi-layered approach that involves both public and private sectors. Businesses need to take a proactive stance on cybersecurity, implementing robust security measures and fostering a culture of cyber awareness. Key steps include:
- Strengthening cyber defenses: This includes implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security tools. Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities and improve defenses.
- Incident response planning: Businesses need to have a well-defined incident response plan in place to deal with cyberattacks effectively. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of an attack, including communication protocols, data recovery procedures, and legal considerations.
- Employee training and awareness: Employees are often the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain. Regular training and awareness programs can help employees recognize phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and other cyber threats.
- Collaboration and information sharing: Sharing threat intelligence and best practices is crucial for staying ahead of the evolving threat landscape. Businesses should collaborate with industry peers, government agencies, and cybersecurity experts to share information and coordinate responses.
- Supply chain security: Businesses need to assess the cybersecurity posture of their suppliers and ensure that they have adequate security measures in place. This may involve conducting security audits of suppliers and incorporating cybersecurity requirements into contracts.
The role of government:
Governments also have a critical role to play in addressing nation-state cyber threats. This includes:
- Developing national cybersecurity strategies: Governments need to develop comprehensive national cybersecurity strategies that address the full spectrum of cyber threats, from espionage to disruption.
- International cooperation: Cyber threats transcend national borders, requiring international cooperation to address effectively. Governments need to work together to share threat intelligence, coordinate incident response, and develop international norms of behavior in cyberspace.
Protecting critical infrastructure: Governments need to work with critical infrastructure operators to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses and protect against nation-state attacks. - Promoting cybersecurity awareness: Governments can play a key role in raising public awareness of cyber threats and promoting cybersecurity best practices.
A shared responsibility
Nation-state cyber threats pose a significant and growing risk to businesses, governments, and individuals. Combating these threats requires a collective effort, with both public and private sectors working together to strengthen cybersecurity defenses, share threat intelligence, and promote a culture of cyber awareness. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, we must remain vigilant and adapt our defenses to stay ahead of the curve. The stakes are high, and the future of our digital world depends on our ability to effectively address this challenge.















Leave a Reply