The fintech sector is experiencing rapid growth and innovation. However, this digital transformation brings increased cybersecurity risks. Fintech companies handle sensitive financial data, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. To protect their customers and their business, fintech companies need to prioritize cybersecurity and implement the right tools. In this article, we’ll explore the top 10 cybersecurity tools for fintech companies. These tools are essential for mitigating cyber risks and ensuring business continuity in today’s dynamic threat landscape.
Firewalls remain a cornerstone of any cybersecurity strategy. They act as the gatekeepers of your network. Essentially, they filter incoming and outgoing network traffic. As a result, they block unauthorized access and prevent malicious actors from infiltrating your systems. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) go a step further. They incorporate advanced features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and deep packet inspection. Therefore, they provide more granular control over network traffic.
While firewalls provide a strong perimeter defense, IDPS solutions take a more proactive approach to security. They continuously monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and known attack signatures. Moreover, they alert security teams to potential threats in real-time. Advanced IDPS solutions can even automatically block or quarantine malicious traffic, preventing attacks before they can cause damage.
Antivirus and antimalware software are fundamental tools for protecting your systems from malicious code. This includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. These solutions use signature-based detection and behavioral analysis to identify and neutralize threats. Ultimately, this prevents them from infecting your systems and compromising data.
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems provide a centralized platform for collecting, analyzing, and correlating security logs and events. These originate from various sources across your network. This enables security teams to gain a holistic view of their security posture. In addition, it allows them to identify potential threats and respond to incidents more effectively. SIEM solutions leverage advanced analytics and machine learning to detect anomalies and suspicious patterns that may indicate an attack.
Data is the lifeblood of fintech companies. Protecting it from unauthorized access and exfiltration is crucial. DLP (Data Loss Prevention) tools help prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization’s control. This includes customer PII, financial records, and intellectual property. These solutions monitor data movement across your network, endpoints, and cloud applications. Furthermore, they identify and block attempts to transfer sensitive data outside authorized channels.
Vulnerability scanners automate the process of identifying security weaknesses in your systems and applications. They scan your IT infrastructure for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software. In turn, they provide you with a prioritized list of security gaps that need to be addressed. Regular vulnerability scanning is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture. It also prevents attacks that exploit known weaknesses.
Encryption is a fundamental security control. It protects data by converting it into an unreadable format. This renders it useless to anyone who doesn’t possess the decryption key. Encryption can be applied to data at rest (stored on devices or servers). Additionally, it can be applied to data in transit (transmitted over networks).
- Data confidentiality: Encryption ensures that even if data is stolen or intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals. This protects customer privacy and sensitive financial information.
- Data integrity: Furthermore, encryption can help prevent data tampering and ensure the integrity of sensitive information.
- Compliance requirements: Many regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, mandate the use of encryption to protect sensitive data.
8. MFA: Strengthening access control
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to the authentication process. It requires users to provide multiple factors of authentication before they can access systems or data. Typically, this involves something the user knows (password), something the user has (security token or mobile device), or something the user is (biometric authentication).
- Protection Against Password Breaches: Even if a user’s password is compromised, MFA prevents attackers from gaining access to their account. This is because they lack the additional authentication factor.
- Reduced Risk of Account Takeover: MFA makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to take over user accounts. This protects both customers and employees from unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Security for Remote Access: With the rise of remote work, MFA is crucial for securing access to company systems and data from outside the corporate network.
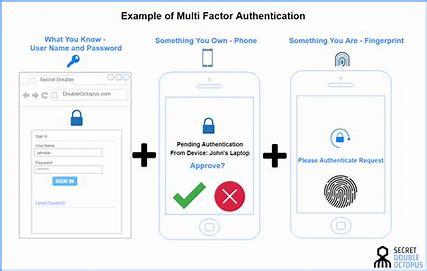
Source: doubleoctopus.com
9. Security awareness training: the human firewall
Employees are often the weakest link in the security chain. Even the most sophisticated security tools can be rendered ineffective if users fall victim to phishing attacks, social engineering, or other forms of manipulation. Security awareness training educates employees about cybersecurity threats, best practices, and company security policies. In essence, it empowers them to make informed decisions and avoid risky behavior.
- Reducing human error: Human error is a leading cause of security breaches. Security awareness training helps reduce the risk of employees falling victim to phishing scams, clicking on malicious links, or inadvertently disclosing sensitive information.
- Promoting a security culture: Regular training fosters a security-conscious culture within the organization. In this culture, employees understand their role in protecting company data. Consequently, they are more likely to report suspicious activity.
- Compliance requirements: Many regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR, require organizations to provide security awareness training to their employees.
10. Threat intelligence for fintechs: staying ahead of cyberattacks
Threat intelligence platforms provide organizations with up-to-date information about the latest cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and attack techniques. This intelligence can be used to proactively improve defenses, prioritize security efforts, and respond to incidents more effectively. Threat intelligence platforms gather data from various sources. These include open-source intelligence (OSINT), commercial threat feeds, and industry collaboration platforms.
- Proactive security: By staying informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities, fintech companies can proactively adjust their security controls and prevent attacks before they occur.
- Targeted defenses: Threat intelligence allows you to tailor your defenses to the specific threats that are most relevant to your industry and organization. This optimizes your security resources.
- Improved incident response: Threat intelligence can help you understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of attackers. This enables you to respond to incidents more effectively and minimize damage.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and investment. By implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that incorporates these 10 tools, fintech companies can significantly strengthen their security posture. They can protect sensitive data and maintain customer trust in an increasingly complex threat landscape. A layered approach to security, combining technology, processes, and people, is essential for effectively mitigating cyber risks and ensuring the long-term success of your fintech business.














Leave a Reply