An analysis of recent cyberattacks, including the MOVEit exploits and rise of deepfakes, reveals evolving ransomware tactics. Organizations must prioritize vulnerability management, enhance ransomware defenses, and strengthen security awareness training to mitigate these growing threats.
The cybersecurity landscape is dynamic, demanding constant vigilance and adaptation. For businesses globally, understanding the nuances of recent cyberattacks is paramount. This analysis dives into recent case studies, dissecting trends and offering practical recommendations.
Deconstructing incidents
Several organizations provide crucial insights into the evolving threat landscape:
-
SANS Institute: SANS’s resources, including research papers and webcasts, offer practical guidance. Their 2024 “Top Attacks and Threats Report” highlighted the growing cost of technical debt and the increasing use of AI in both attacks and defense. The reported 73% surge in ransomware cases underscores the urgency of addressing this threat. A previous SANS study detailing a telecommunications company’s post-breach recovery provides a valuable real-world example of incident response.
-
Verizon DBIR: The DBIR, analyzing thousands of security incidents, offers a data-driven perspective. The 2024 report’s finding of a 180% increase in vulnerability exploitation, likely linked to zero-day exploits like those targeting MOVEit, emphasizes the critical need for proactive patching. The DBIR also reinforces the persistent challenges of ransomware, the human element in breaches, and the rising risks associated with third-party vendors. The report’s sector-specific insights, such as the 2021 finding of public administration’s vulnerability to ransomware, highlight the importance of tailored security strategies.
-
NIST: NIST’s resources, including the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), provide valuable guidance. A NIST case study showcasing an energy company’s successful implementation of the CSF demonstrates the framework’s practical application. NIST’s focus on resources for small businesses, addressing threats like ATM skimming and social engineering, acknowledges the diverse needs of organizations.
Case studies in focus
A review of recent incidents reveals recurring attack vectors and impacts: Case study links
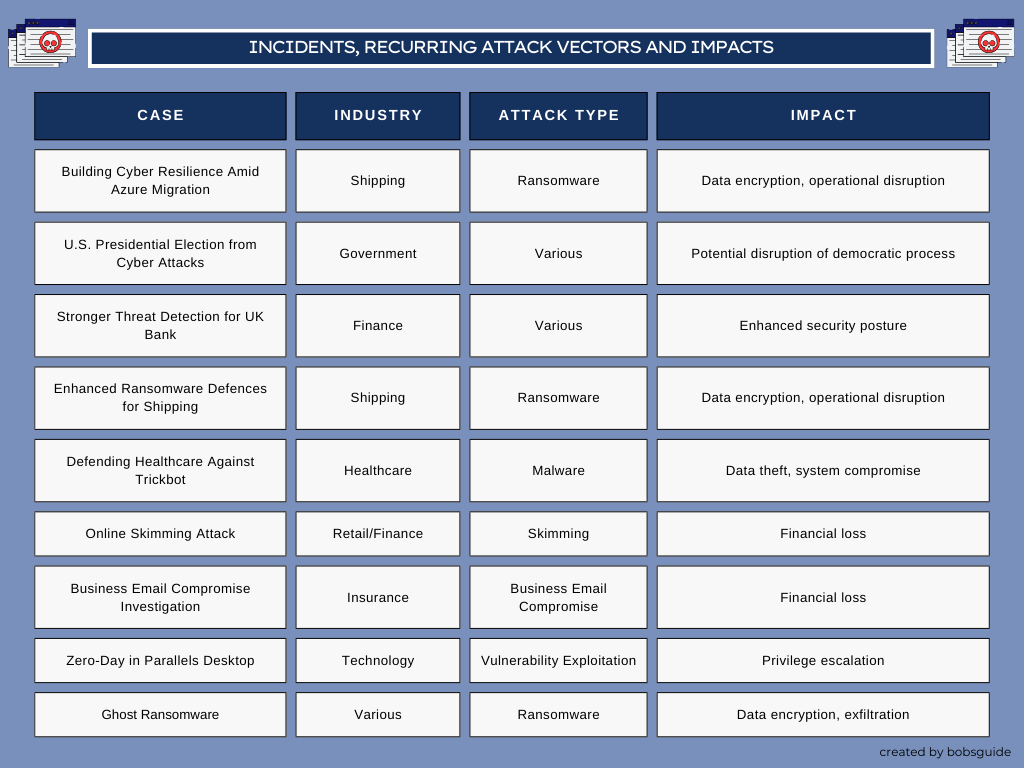
(This table is a representative sample; numerous other incidents occur across sectors.)
Unpacking the Evolving Threat Landscape
The cybersecurity landscape is in constant flux, with new threats and attack vectors emerging regularly. Analyzing recent incidents reveals several key trends that demand attention:
1. The Sophistication of Vulnerability Exploitation: Attackers are not simply targeting any vulnerability; they are increasingly focused on exploiting vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems and applications, often leveraging zero-day exploits for maximum impact. The MOVEit attacks serve as a stark reminder of this trend. This highlights the need for organizations to go beyond basic vulnerability scanning and patching. Proactive measures such as penetration testing, red teaming exercises, and continuous security monitoring are crucial to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
2. Ransomware’s Multifaceted Approach: Ransomware has evolved into a multi-pronged threat. While encryption remains a core tactic, attackers are increasingly exfiltrating sensitive data before deploying ransomware, adding the threat of public exposure to their arsenal. This tactic puts pressure on organizations even if they have robust backups. To combat this, organizations need to adopt a holistic approach to ransomware defense, encompassing data backups, incident response plans, and security awareness training, along with data loss prevention (DLP) solutions and network segmentation to limit the impact of data exfiltration.
3. The Persistent Human Element: Despite technological advancements, human error and manipulation remain significant factors in cybersecurity breaches. Phishing attacks, social engineering, and insider threats continue to plague organizations. This underscores the critical importance of comprehensive security awareness training that goes beyond simple awareness and focuses on behavioral change. Simulations, gamification, and interactive training modules can help employees recognize and respond to threats effectively.
4. The Expanding Threat Surface of Supply Chains: Supply chain attacks are on the rise, exploiting the interconnectedness of modern businesses. Attackers target vulnerabilities in third-party vendors and suppliers to gain access to their ultimate targets. This emphasizes the need for robust vendor risk management programs that include thorough security assessments, contractual obligations for security practices, and ongoing monitoring of vendor security posture.
5. The Rise of AI-Powered Attacks: Attackers are leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate attacks, evade detection, and increase their effectiveness. AI-powered attacks can generate sophisticated phishing lures, create polymorphic malware, and even automate the discovery of vulnerabilities. To counter this, organizations must adopt AI-driven security tools that can analyze vast amounts of data, identify anomalies, and respond to threats in real-time.
6. Deepfakes: The New Frontier of Deception: Deepfake technology, which uses AI to create realistic fake videos or audio, is rapidly emerging as a powerful tool for cybercriminals. Deepfakes can be used for social engineering, spreading misinformation, manipulating individuals, and damaging reputations. Organizations need to be aware of this threat and develop strategies to detect and mitigate the risks of deepfakes, including media forensics and authentication technologies.
7. Emerging Threats on the Horizon: Looking ahead, cybersecurity leaders anticipate a complex threat landscape shaped by several factors:
- Supply Chain Complexities: The increasing complexity of supply chains and lack of visibility into supplier security practices pose significant challenges.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Rising geopolitical tensions increase the risk of cyber espionage, intellectual property theft, and disruption of critical infrastructure.
- AI Adoption Risks: Organizations often lack proper assessment processes for AI tools before deployment, creating potential security vulnerabilities.
- Generative AI and Cybercrime: The accessibility of generative AI tools is fueling more sophisticated social engineering attacks, phishing campaigns, and ransomware attacks.
- Regulatory Challenges: The fragmentation of cybersecurity regulations across jurisdictions creates compliance challenges for multinational organizations.
- Cyber Talent Shortage: The widening gap in cybersecurity skills leaves organizations struggling to find and retain qualified professionals.
These trends underscore the need for organizations to adopt a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity, continuously assessing their risk profile, implementing robust security controls, and staying informed about the evolving threat landscape.
Building a Resilient Cybersecurity Posture
In light of these trends, organizations need to take proactive steps to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses:
1. Prioritize Vulnerability Management
Implement a robust vulnerability management program that includes:
- Continuous Scanning and Assessment: Regularly scan systems and applications for vulnerabilities, prioritizing internet-facing assets.
- Timely Patching: Deploy patches promptly to address known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Conduct regular penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify vulnerabilities.
- Red Teaming Exercises: Engage red teams to emulate adversary tactics and test the effectiveness of security controls.
- Configuration Management: Implement strong configuration management practices to ensure systems are securely configured.
2. Enhance Ransomware Defenses
Develop a comprehensive ransomware preparedness plan that includes:
- Data Backups: Implement regular and secure data backups, ensuring they are offline and immutable.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response to1 ransomware attacks.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about phishing, social engineering, and other tactics used in ransomware attacks.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Deploy DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the network.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the network to limit the lateral movement of attackers and contain the impact of ransomware.
3. Strengthen Security Awareness Training
Invest in comprehensive security awareness training that focuses on behavioral change and includes:
- Phishing Simulations: Conduct regular phishing simulations to test employee awareness and reinforce best practices.
- Social Engineering Awareness: Educate employees about social engineering tactics and how to identify and avoid them.
- Interactive Training Modules: Use interactive training modules to engage employees and make learning more effective.
- Gamification: Incorporate gamification elements to make training more engaging and encourage participation.
- Regular Refresher Training: Provide regular refresher training to keep security awareness top of mind.
4. Mitigate Supply Chain Risks
Implement a robust vendor risk management program that includes:
- Security Assessments: Conduct thorough security assessments of all vendors and suppliers, especially those with access to sensitive data.
- Contractual Obligations: Include security requirements in contracts with vendors and suppliers.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor the security posture of vendors and suppliers.
- Information Sharing: Establish channels for sharing threat intelligence with vendors and suppliers.
5. Embrace AI-Powered Security
Incorporate AI and ML technologies into your security strategy to:
- Enhance Threat Detection: Use AI-powered tools to analyze vast amounts of data and identify anomalies that may indicate an attack.
- Automate Response: Automate incident response processes to accelerate response times and contain the impact of attacks.
- Improve Vulnerability Management: Use AI to prioritize vulnerabilities and identify areas of greatest risk.
- Combat AI-Powered Attacks: Deploy AI-powered defenses to counter the growing sophistication of AI-driven attacks.
6. Address the Deepfake Threat
Develop strategies to detect and mitigate the risks of deepfakes, including:
- Media Forensics: Invest in media forensics tools and techniques to authenticate the legitimacy of videos and audio recordings.
- Authentication Technologies: Implement authentication technologies that can verify the identity of individuals in videos and audio recordings.
- Employee Awareness: Educate employees about deepfakes and how to identify them.
7. Prepare for Emerging Threats
Stay informed about emerging threats and adapt your security strategy accordingly:
- Monitor Threat Intelligence: Continuously monitor threat intelligence feeds and industry reports to stay abreast of the latest threats.
- Invest in Research and Development: Invest in research and development to stay ahead of the curve and develop innovative security solutions.
- Build a Culture of Agility: Foster a culture of agility and adaptability to respond quickly to new and evolving threats.
- Address the Cyber Talent Shortage: Invest in training and education to develop the next generation of cybersecurity professionals.
A Continuous Commitment
Cybersecurity is not a one-time fix but an ongoing commitment. By understanding the evolving threat landscape, implementing robust security measures, and fostering a culture of security awareness, UK and US businesses can mitigate risks and protect their valuable assets. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential in this dynamic environment.














Leave a Reply