The digital age has ushered in unprecedented interconnectedness and efficiency for financial institutions, but it has also exposed them to a new breed of cyber threats, with ransomware reigning supreme. Falling victim to a ransomware attack is no longer a question of ‘if’ but ‘when,’ and the financial sector, with its treasure trove of sensitive data and critical infrastructure, is a prime target. While basic data recovery strategies are often discussed, the reality of ransomware recovery is far more intricate, demanding a proactive, multi-layered approach that goes beyond the obvious.
Beyond backups: rethinking data recovery in the age of ransomware
Traditional data recovery strategies, primarily focused on backups and restoration, are no longer sufficient in the face of modern ransomware tactics. Today’s cybercriminals are sophisticated, employing a multi-pronged approach that includes data exfiltration, DDoS attacks, and the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities. This demands a paradigm shift in how financial institutions approach data recovery, one that anticipates and mitigates the evolving threat landscape.
The pillars of advanced ransomware recovery
1. Proactive Threat Hunting: Turning the Tables on Attackers
- Shift from reactive to proactive security. Rather than waiting for an attack to occur, proactive threat hunting involves actively searching for malicious activity within your network.
- Utilize machine learning for enhanced detection. Leverage advanced threat detection tools that employ machine learning algorithms to identify anomalous behavior and potential indicators of compromise.
- Establish a dedicated threat hunting team. This team should continuously monitor the network, investigate suspicious activity, and proactively identify and neutralize threats before they can escalate.
2. Immutable Backups: Shielding Your Data from Ransomware’s Grasp
- Ensure the integrity of your backups. Immutable backups cannot be modified or deleted by ransomware, guaranteeing that you always have a clean copy of your data to restore from.
- Explore diverse backup solutions. Cloud-based backup solutions with object lock functionality provide immutability, while on-premises solutions with write-once-read-many (WORM) storage offer similar protection.
3. Multi-Layered Recovery Architecture: The Fortress Approach
- Diversify your recovery strategy. A multi-layered recovery architecture incorporates on-premises backups, off-site backups, and cloud-based backups, ensuring redundancy and minimizing the risk of losing all your backups in a single attack.
- Implement the 3-2-1 backup strategy. This strategy recommends having 3 copies of your data on 2 different media, with 1 copy stored off-site for added protection.
4. Data Recovery Orchestration: Automating Your Way to Resilience
- Streamline the recovery process. Data recovery orchestration tools automate the recovery process, reducing downtime and accelerating recovery time.
- Define clear objectives. Establish recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for critical systems and data to ensure business continuity.
- Test and refine your plan. Regularly test and refine your recovery orchestration plan to ensure it meets your business needs and can effectively respond to evolving ransomware tactics.
5. Negotiation and Incident Response: Navigating the Aftermath
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a ransomware attack, including communication protocols, containment strategies, and recovery procedures.
- Engage with experts. Consider involving law enforcement and cybersecurity experts to assist with negotiation and recovery efforts, especially in complex or high-impact attacks.
6. Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Empowering Your Human Firewall
- Educate your employees. Provide regular cybersecurity awareness training to educate employees about ransomware threats, phishing scams, and best practices for prevention.
- Conduct phishing simulations. Phishing simulations test employee awareness and reinforce training, helping to identify and address vulnerabilities in human behavior.
- Foster a culture of cybersecurity. Encourage employees to report suspicious activity and actively participate in maintaining a secure work environment.
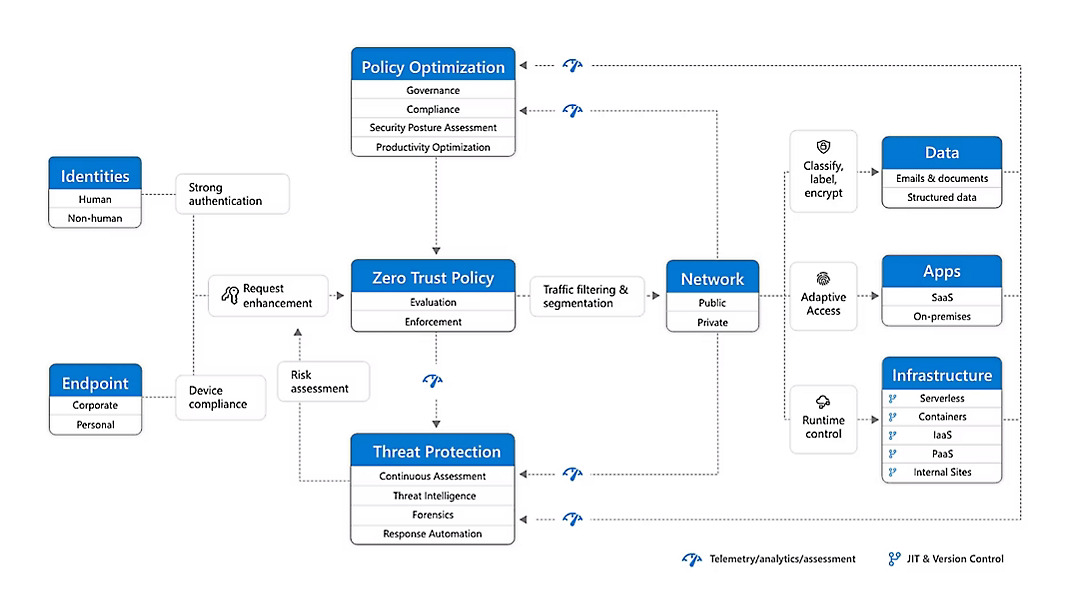
7. Zero Trust Security Framework: Trust No One, Verify Everything
- Adopt a Zero Trust approach. A Zero Trust security framework assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, enforcing strong authentication, authorization, and access controls to limit the lateral movement of attackers.
- Segment your network. Network segmentation isolates critical systems and data from less sensitive areas, preventing the spread of ransomware and minimizing the impact of an attack.
8. Vulnerability Management: Staying Ahead of the Curve
- Establish a robust vulnerability management program. This program should proactively identify and remediate vulnerabilities in systems and applications, reducing the attack surface for ransomware.
- Conduct regular security assessments. Vulnerability scans and penetration testing assess your security posture and identify potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
- Prioritize patching. Ensure timely updates and security patches are applied to critical systems and applications, addressing known vulnerabilities and mitigating the risk of ransomware attacks.
9. Cyber Insurance: Transferring the Risk
- Consider cyber insurance. Cyber insurance can help mitigate financial losses associated with a ransomware attack, covering costs related to data recovery, legal expenses, and business interruption.
- Review policy terms carefully. Ensure your cyber insurance policy provides adequate coverage for ransomware-related incidents, including data exfiltration and DDoS attacks.
- Develop an incident response plan. Work with your insurer to develop a comprehensive incident response plan that aligns with your policy requirements and ensures a smooth recovery process.
10. Collaboration and Threat Intelligence Sharing: Strength in Numbers
- Join the fight against ransomware. Participate in industry threat intelligence sharing initiatives to stay informed about emerging ransomware threats and tactics.
- Share your knowledge. Collaborate with other financial institutions and cybersecurity organizations to share best practices, lessons learned, and threat intelligence.
- Leverage threat intelligence feeds. Threat intelligence feeds provide valuable insights into the latest ransomware trends, helping you proactively identify and mitigate potential attacks.
Responding to a ransomware attack requires a swift and organized approach. This checklist outlines the crucial steps financial institutions should take immediately upon detecting an attack to minimize damage, preserve evidence, and ensure business continuity
Embracing a proactive and resilient approach
Ransomware attacks are a persistent and evolving threat to the financial sector, demanding a proactive and multi-faceted approach to data recovery. By implementing advanced strategies, embracing a Zero Trust security framework, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, financial institutions can navigate the labyrinth of ransomware recovery and emerge stronger and more resilient. The key is to go beyond the basics, anticipate the evolving threat landscape, and invest in comprehensive cybersecurity measures that safeguard sensitive data, ensure business continuity, and protect the integrity of the financial ecosystem.














Leave a Reply